April 2026 AVAPS Group Meeting Registration Now Open

Spring 2026 Radar Technology Workshop
Registration Now Open
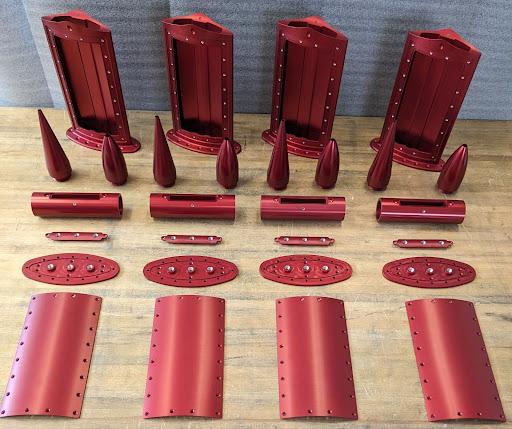

Transforming Scientific Vision into Reality: EOL's Design and Fabrication Services
For nearly six decades, the NSF NCAR Earth Observing Laboratory has stood at the forefront of atmospheric science innovation. At the heart of this innovation lies our Design and Fabrication Services (DFS), a comprehensive engineering and manufacturing facility that transforms cutting-edge scientific concepts into precision instruments that advance our understanding of Earth's atmosphere.
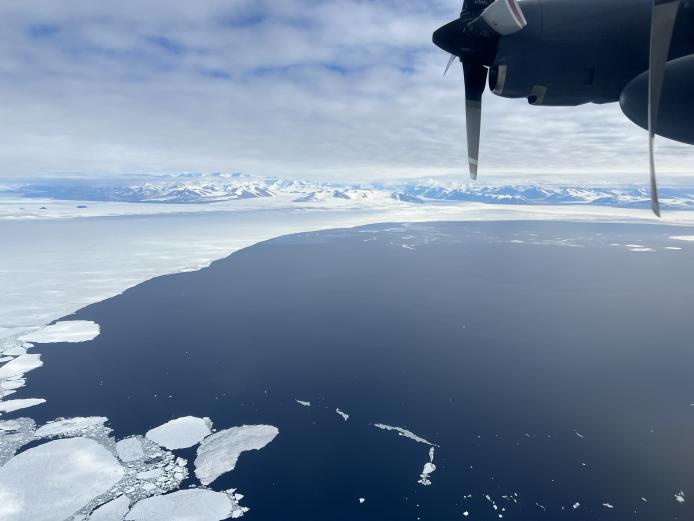

Atmospheric instrument hitches ride on Antarctic planes
The Southern Ocean plays a fundamental role in the global carbon cycle, yet air-sea fluxes of CO2 in the region, and their driving processes, are highly uncertain. The Southern Ocean Carbon Gas Observatory (SCARGO) is an NSF Office of Polar Programs funded study led by NSF NCAR in collaboration with NOAA, CIRES, CWorthy, and Earth Sciences New Zealand.
NSF NCAR EOL Field Project Page
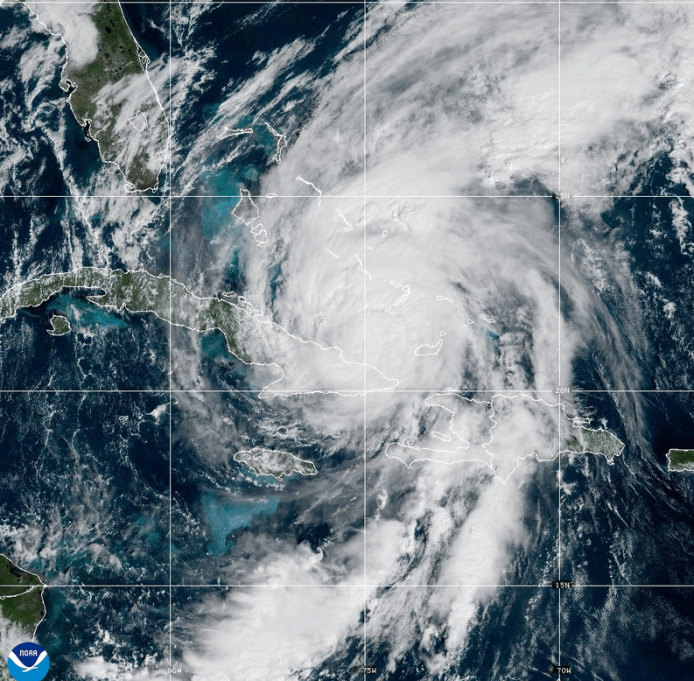
Record-Breaking Winds confirmed for Hurricane Melissa
As Hurricane Melissa approached Jamaica on October 28, 2025, a NOAA Hurricane Hunter aircraft equipped with an NSF NCAR AVAPS™ dropsonde system released a series of high-precision Vaisala dropsondes into the storm. Just before one sonde reached the ocean surface, it captured an extraordinary 252-mph wind gust—the strongest ever recorded by a dropsonde. This moment underscores the vital partnership between NOAA’s hurricane reconnaissance mission and NSF NCAR’s leadership in dropsonde technology. Other News sources
Photo: NOAA/NESDIS/STAR GOES-19 satellite image
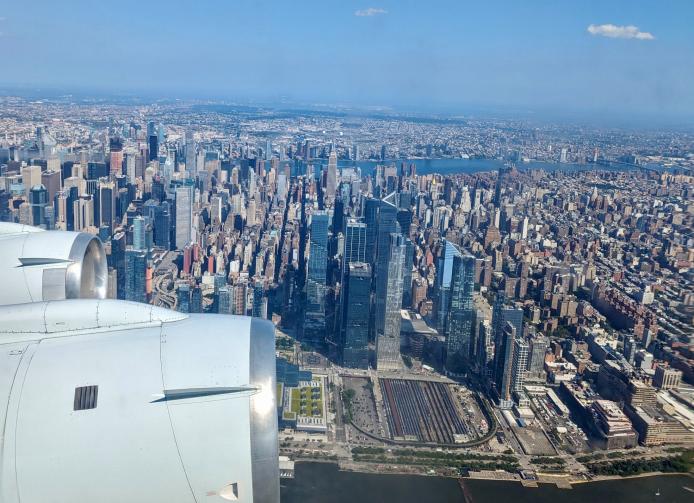

GOTHAAM
Skimming the Skyline: Scientists Track Urban Emissions Over New York City
NSF NCAR EOL successfully supported a research effort to investigate what's in the air above one of the most populated and chemically complex regions in North America.
Photo: Mike Robinson
EOL in the News
Read stories and articles about the incredible work by EOL staff and our suite of requestable Lower Atmosphere Observing Facilities (LAOF).

NSF Facility and Instrumentation Request Process (FIRP)
The Facility and Instrumentation Request Process (FIRP) solicitation describes the mechanism by which the research community can propose projects that require access to facilities and instrumentation sponsored by the Facilities for Atmospheric Research and Education (FARE) Program in the Division of Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences (AGS). Specialized FARE instrumentation and facilities include the Lower Atmosphere Observing Facilities (LAOF) and the Community Instruments and Facilities (CIF). For more information, please contact Nick Anderson, NSF Program Director (AGS-PDM@nsf.gov).

Explore NCAR-managed Lower Atmosphere Observing Facilities for your field research
EOL manages and operates a portfolio of multi-user national facilities that are sponsored by NSF. The NCAR-managed Lower Atmosphere Observing Facilities include:
These specialized facilities and instrumentation can be requested to carry out the scientific field work associated with the investigation of a wide range of geophysical phenomena.